Tax Forms
After January 1st, 2023, the new W-4P tax form is required by the IRS for taxation of annuity payments. Or if you are planning on taking required minimum distribution, lump sum payment, or rollover from your account, you may need to complete a W-4R. Complete the W-4N to establish, make changes to, or request exemption from Nebraska State tax withholding.
If you are thinking about accessing these options, you may want to familiarize yourself with these forms at the IRS.GOV website. The instruction sheets on these forms are comprehensive and helpful. NPERS staff are not allowed to provide taxation advisement or guidance, so you may need to take these forms to your tax advisor for review, prior to requesting a distribution or annuity payment.
Federal Tax Forms
- W-4P View Form (W-4P Walkthrough Video)
- W-4R View Form
State Tax Form
- W-4N View Form
W4 Tax Forms
In this video, we explain the three different federal W-4 forms and how they apply when you retire, return to work, or have multiple sources of taxable income. We'll discuss when each form is required, common mistakes to avoid, and how these forms work together to help ensure the correct amount of federal income tax is withheld. This is especially important for retirees who continue working or receive income from more than one source. This video is for general educational purposes only and is not intended as tax advice. For guidance specific to your situation, consider consulting a licensed tax professional.
Understanding Your 1099-R
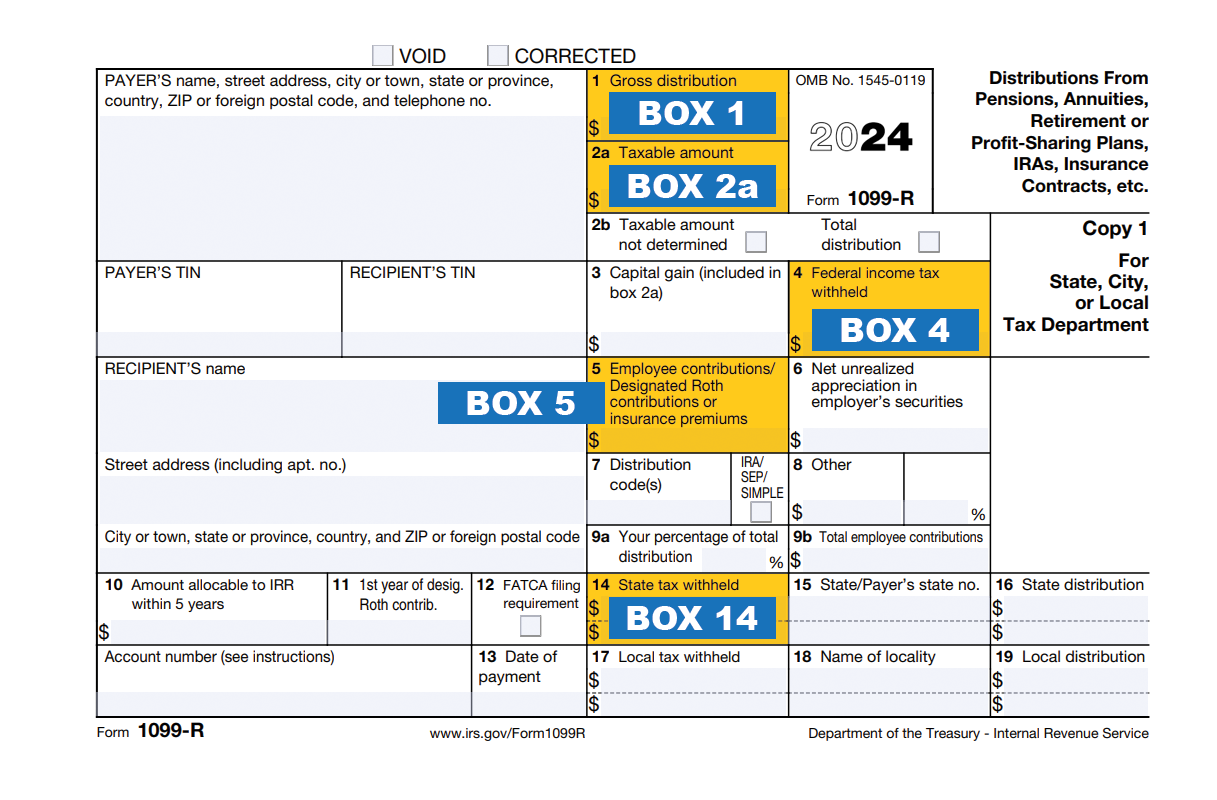
| BOX 1 | Box 1 shows everything NPERS paid you in 2025. |
| BOX 2a | Box 2 a shows the amount that is taxable to you. |
| BOX 4 | Box 4 shows the amount that was withheld for federal taxes. |
| BOX 5 | Box 5 shows the amount that is not taxable. |
| BOX 14 | Box 14 shows the amount that was withheld for state taxes. |
| NOTE: | BOX 1 - BOX 2a = BOX 5 |
Tax Estimator 2026
In this video, we demonstrate how to use the NPERS Tax Estimator to determine whether additional federal income tax withholding may be needed in retirement, especially if you continue working after you retire. By comparing taxes on your annuity, your wages, and your combined income, you can make more informed withholding decisions and reduce the risk of owing money at tax time.